Linux Basics
Linux is an open-source Unix-like Operating System (OS) based on the Linux kernel, an OS kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution. Distributions include the Linux kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Linux is one of the very few open source OS, where the kernel acts as the central unit of operation for establishing the communication between the computer hardware and the system software.
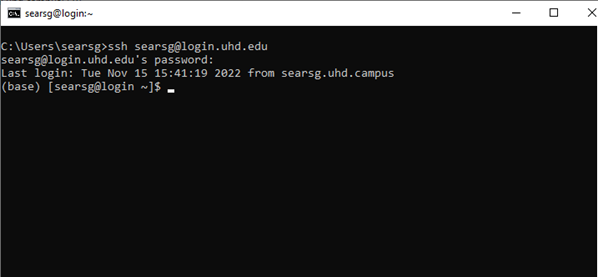
The Linux command line is a text interface to your computer. Often referred to as the shell (bash), terminal, console, or command prompt, this is the interface for navigating through Linux. This is what a terminal looks like. This is how you will be navigating through the HPC cluster.
This may sound complicated and confusing, but with a little practice and some basic commands, you will be able to navigate with ease. Here are a few basic commands to navigate through UHD's HPC cluster.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| man <command> | Shows the manual pages for the command entered “ex. $man ls" |
| pwd | Print Working Directory, pwd will print the full path of current/working directory |
| ls | List directory contents |
| ls -a | List all the content, including hidden files |
| ls -l | List the content and its information |
| mkdir <foldername> | Creates a new directory labeled “foldername" inside the current working directory |
| cd <path/foldername> | Change Directory, this changes the current directory to the path given |
| cd | Return to $HOME directory |
| cd .. | Go up a directory |
| nano, vim | Text editors |
| cp <source destination> | Copy source to destination |
| cp -r <source destination> | Copy a directory recursively from source to destination |
| mv <source destination> | Move (or rename) a file from source to destination |
| rm <file> | Remove file |
| rm -r <folder> | Remove a directory and its contents recursively |
| cat <file> | Print contents of file on the screen |
| less <file> | View file and navigate through file |
| head <file> | Show first 10 lines of file |
| tail <file> | Show last 10 lines of file |
| diff <file1.txt> <file2.txt> | Command to compare the contents of two files and displays the differences |
| df -h | Reports file system disk space usage in human readable form. |
This may sound complicated and confusing, but with a little practice and some basic commands, you will be able to navigate with ease. Here are a few basic commands to navigate through UHD's HPC cluster.
<< Getting Started Text Editors >>